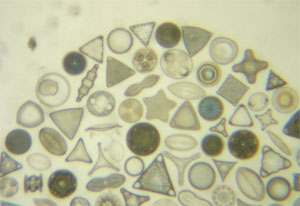
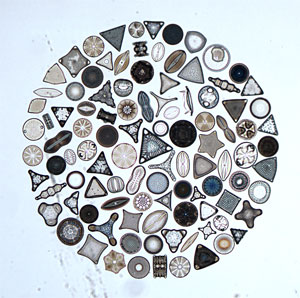
Diatoms imaged using the low magnification objective ("2")
Modern compound microscope (5x objective).
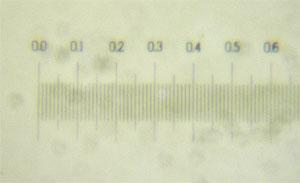
Micrometer scale imaged using the low magnification objective ("2").
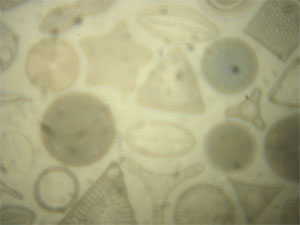

Diatoms imaged using the low + high magnification objectives ("2" + "3")
Modern compound microscope (10x objective).
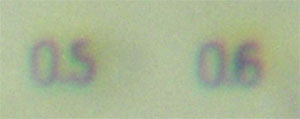
Chromatic aberration exhibited by the optics of the pocket microscope produces these color fringes. The long wavelength light (red) focuses at a different position than the short wavelength light (blue). The difference in focus positions produces color fringes around objects.